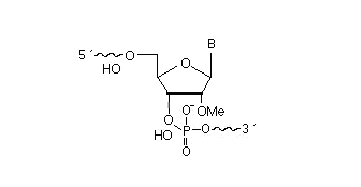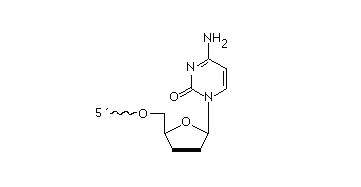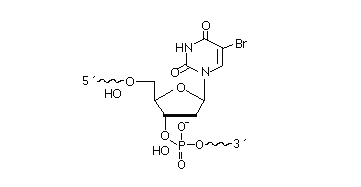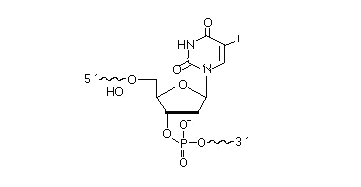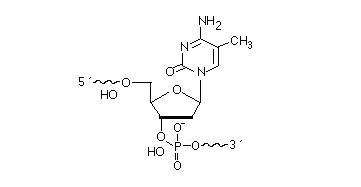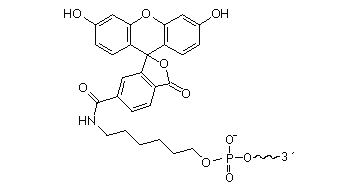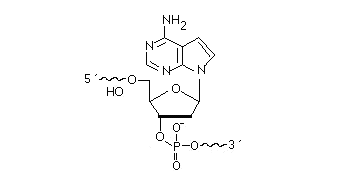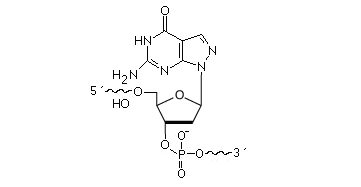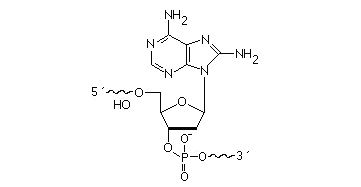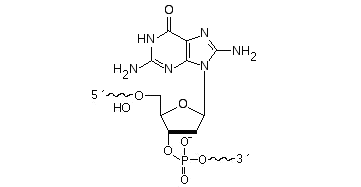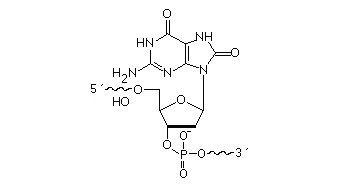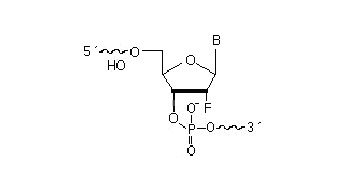
 2’F-RNA
2’F-RNA
2'-F-RNA is even more stable than 2'-O-methyl-RNA. 2'-F-RNA & RNA duplexes do not activate RNase H and are more stable (with higher Tm) than RNA & 2'-O-methyl-RNA duplexes. It serves mainly for antisense applications. May be attached anywhere within the oligonucleotide sequence.